Understanding the Genetic Counseling Process
October 4, 2025
The Role of Regular Cardiology Check-ups for Heart Health
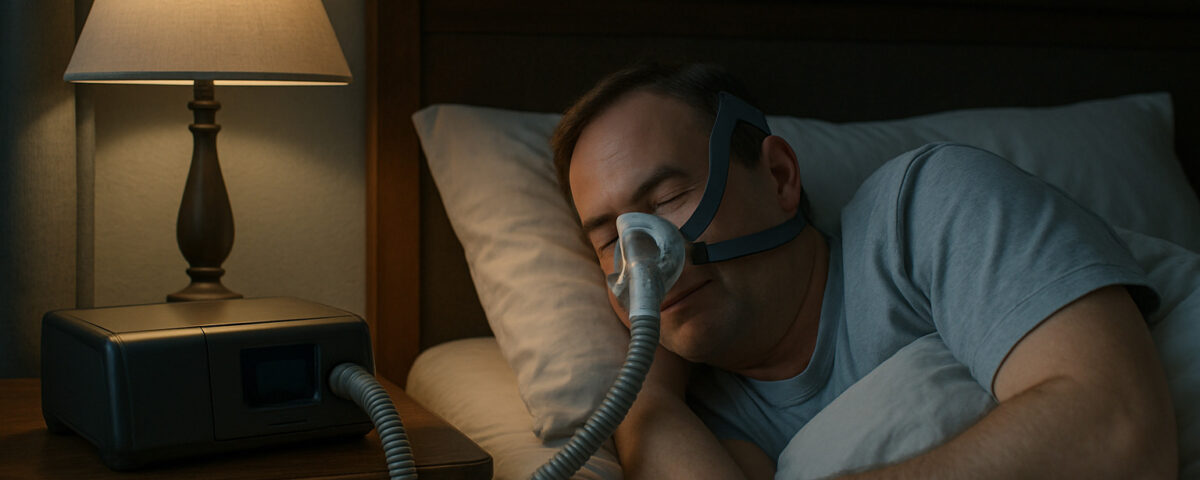
October 6, 2025When sleep is consistently disrupted, it can affect daily functioning, from concentration levels to physical energy. For individuals who suspect they may have a sleep disorder, obtaining a proper diagnosis is the first step toward management. Home sleep testing offers a convenient method for gathering information about breathing patterns during sleep. This can help a clinician in the diagnostic process for conditions like sleep apnea.
What Is Home Sleep Testing?
A home sleep test is a simplified sleep study performed outside of a specialized sleep laboratory. It is a diagnostic tool prescribed by a healthcare provider to screen for or diagnose certain sleep-related breathing disorders. The home sleep testing apparatus typically includes several sensors that monitor key biological functions during sleep. These often measure:
- Breathing Patterns: Sensors track airflow and respiratory effort. This data helps identify interruptions or reductions in breathing.
- Oxygen Saturation: A pulse oximeter measures the level of oxygen in the blood. Drops in blood oxygen levels are a common indicator of breathing cessations.
- Heart Rate: The pulse oximeter also records heart rate, as changes in heart rhythm can occur in response to breathing disruptions.
- Snoring: Some devices include a microphone to record the intensity and frequency of snoring. This is a common symptom associated with sleep apnea.
The individual then wears the device for one or more nights as directed. After the testing period, the device is returned, and the recorded data is downloaded and analyzed by a qualified sleep specialist.
What Is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep. When breathing stops, the brain briefly rouses the person from sleep to resume breathing. The individual may be unaware of these awakenings. There are two main types of sleep apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the more common form. It occurs when the muscles in the back of the throat relax excessively. This causes the soft tissue to collapse and block the upper airway during sleep.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): This form is less common and happens when the brain fails to send the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing.
Common symptoms include loud and persistent snoring, episodes of breathing cessation during sleep, and excessive daytime fatigue. Other symptoms can consist of morning headaches, difficulty concentrating, and mood changes.
What Are the Benefits of Testing?
When a clinician determines it is appropriate, home sleep testing provides several advantages for individuals being evaluated for sleep apnea. One of the primary benefits is accessibility and convenience. Patients can perform the test in their own bed, which eliminates the need to travel to and spend the night in an unfamiliar sleep laboratory. This type of sleep testing can be a more cost-effective option compared to in-lab polysomnography.
For many individuals with suspected moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea, HSTs are a reliable diagnostic tool. The data collected provides sufficient information for a clinician to confirm a diagnosis and recommend a course of action. When the results are inconclusive or if a more complex sleep disorder is suspected, the test can guide the next steps.
Seek Professional Sleep Disorder Care
Home sleep testing is a valuable method for gathering data about sleep-related breathing, but it is one part of a comprehensive diagnostic process. The interpretation of test results requires the expertise of a sleep specialist, and the results must be reviewed in the context of a person’s complete medical history and symptoms. A healthcare provider can determine if a home sleep test is the right choice or if an in-lab study is more appropriate for a specific situation.