What To Look for in a Quality Vascular Specialist
September 18, 2025
Gallbladder Surgery and Its Effect on Weight Management
September 18, 2025Skin cancer remains one of the most common forms of cancer in America, with significant links to prolonged sun exposure and ultraviolet (UV) radiation. However, the risk of developing skin cancer can be effectively reduced through the adoption of proper sun safety measures. Understanding the factors that contribute to UV damage and implementing protective strategies are essential steps in minimizing harm to the skin. Here are a few tips and evidence-based recommendations to promote sun safety through dermatology and aid in skin cancer prevention:
Applying Sunscreen Correctly
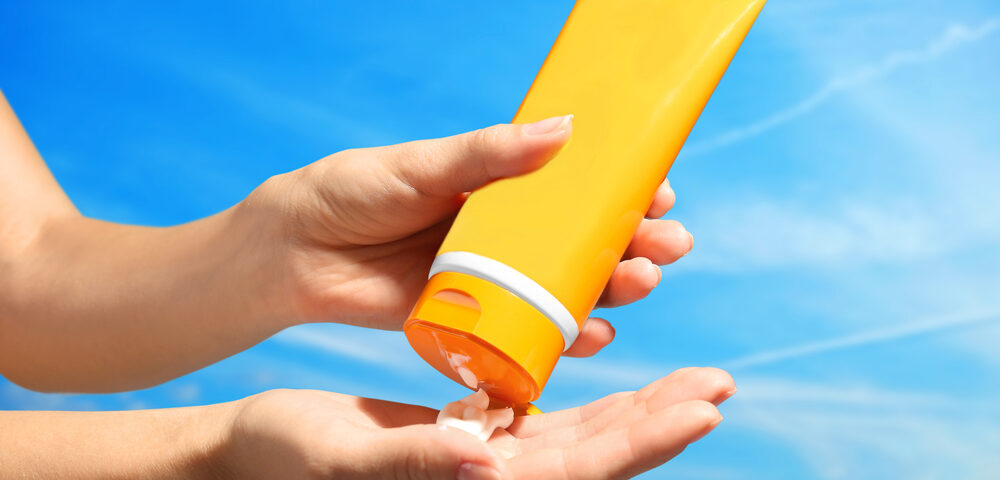
Skin cancer prevention is a key part of dermatology practice. Sunscreen is a topical product that absorbs or reflects a portion of the sun’s ultraviolet radiation. For effective use, select a broad-spectrum sunscreen, which provides protection against both UVA and UVB rays, with an SPF of 30 or higher. Apply sunscreen generously to all exposed skin approximately 15 to 30 minutes before going outdoors. This allows the product time to bind to the skin.
Commonly overlooked areas include the ears, neck, tops of feet, and the back of the hands. Reapplication is a fundamental component of sunscreen efficacy. You should reapply sunscreen at least every two hours, or more frequently after swimming, sweating, or towel drying. Lip balm with SPF protection is also recommended to protect the lips. The consistent and correct application of sunscreen is a primary component of sun safety.
Utilizing Protective Clothing
Physical barriers offer a direct method of sun protection. Clothing is one of the most effective forms of shielding the skin from UV rays. You can choose long-sleeved shirts and long pants made from tightly woven fabrics for maximum coverage. Some garments are specifically designed for sun protection and carry an Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) rating, which indicates how much UV radiation can penetrate the fabric.
In addition to clothing, a wide-brimmed hat provides shade for the face, scalp, ears, and neck. A brim of at least three inches all around is suggested for adequate coverage. Sunglasses that block 99% or more of UV radiation protect the eyes and the delicate skin surrounding them. Using these physical coverings in conjunction with sunscreen creates a more comprehensive defense against sun exposure.
Modifying Behavioral Factors
Modifying daily habits can significantly reduce overall UV exposure. The sun’s rays are most intense between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. When possible, limit direct sun exposure during these peak hours. Seeking shade under a tree, umbrella, or other shelter is a simple and effective protective measure.
Be mindful that UV rays can penetrate clouds and reflect off surfaces like water, sand, snow, and pavement. This means sun protection is necessary even on cloudy days or in shaded areas. Awareness of the daily UV Index, which forecasts the intensity of UV radiation, can also help you plan outdoor activities and take appropriate precautions. These behavioral adjustments are a foundational aspect of a sun-safe lifestyle.
Learn More About Dermatology
An approach to sun safety involves multiple layers of protection. This includes the correct and consistent application of broad-spectrum sunscreen. It also involves wearing protective clothing, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses to create physical barriers. Modifying behaviors by seeking shade and avoiding peak sun hours further reduces UV exposure. These combined strategies form a practical framework for skin protection.