Tips for Lifelong Weight Loss Maintenance
October 1, 2025
The Benefits of Regular Podiatrist Check-Ups
October 1, 2025Athletes face a range of physical challenges that can sometimes lead to unexpected setbacks. Sports injuries can occur at all skill levels, from weekend warriors to professional competitors. Being aware of these risks helps athletes make informed decisions about participation and recovery. Here are a few things about understanding the risks of sports injuries:
Common Types of Injuries
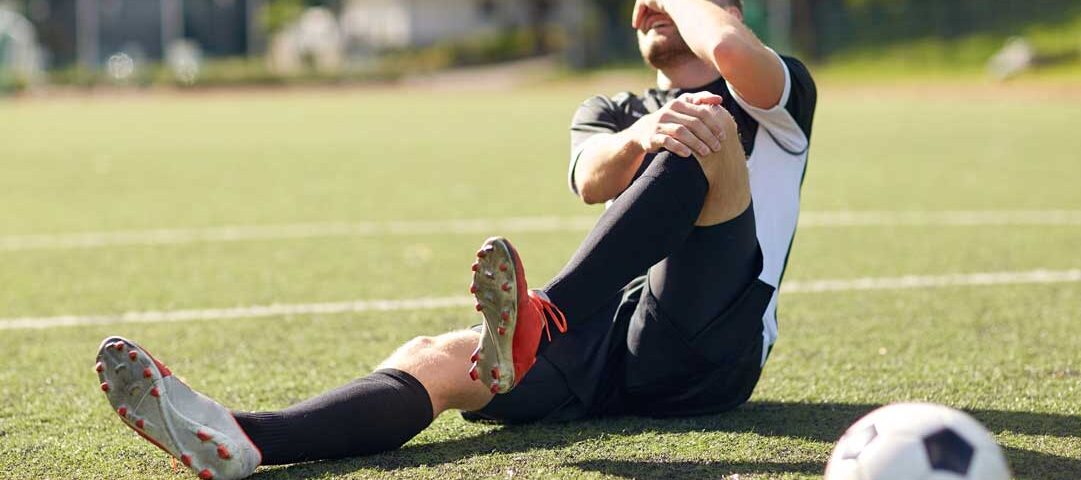
Sports activities put stress on various body parts, often resulting in predictable injuries. Knee injuries, such as ACL, MCL, and PCL tears, are common and affect joint stability. Shoulder injuries include rotator cuff tears, impingement, and labral tears from repetitive motion or trauma. Lower leg injuries, such as Achilles tears, ankle sprains, and shin splints, frequently affect runners and jumping athletes. Upper body injuries include tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, biceps tears, and finger injuries from contact or overhead sports.
Common sports-related injuries include:
- ACL, MCL, and PCL knee ligament tears
- Rotator cuff tears, shoulder impingement, and labral tears
- Achilles tendon tears, ankle sprains, and shin splints
- Tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, biceps tears, and finger injuries
Understanding these injury patterns can help athletes and coaches develop practical training, prevention, and recovery strategies.
Risk Factors Athletes Face
Several factors may increase an athlete’s likelihood of experiencing sports injuries. Age plays a role, as older athletes may have decreased flexibility and slower recovery times. Previous injuries can create weakness or instability, making re-injury more likely. Training methods also affect risk, as sudden increases in intensity or duration can overwhelm tissues, while inadequate warm-ups and poor technique place abnormal stress on muscles and joints.
Equipment and environmental conditions further contribute to injuries. Worn or improperly fitted gear may not provide sufficient protection, and uneven or unsafe playing surfaces increase the risk of falls or twists. Footwear that does not match the sport or surface may affect stability and traction. Environmental factors, such as hot or cold weather, poor lighting, and wet surfaces, can increase fatigue, reduce flexibility, and create additional hazards for athletes.
Body Systems Most Affected
Several factors increase an athlete’s risk of injury, including age, previous injuries, and training methods. Sudden increases in intensity, inadequate warm-ups, and poor technique may place abnormal stress on muscles and joints. Equipment issues, such as worn or improperly fitted gear and unsuitable footwear, can reduce protection and stability. Playing surfaces in poor condition, along with environmental factors such as hot or cold weather, inadequate lighting, and wet conditions, also contribute to an increased risk of injury. Being aware of these factors can help athletes take steps to reduce potential injuries.
Treatment Approaches Available
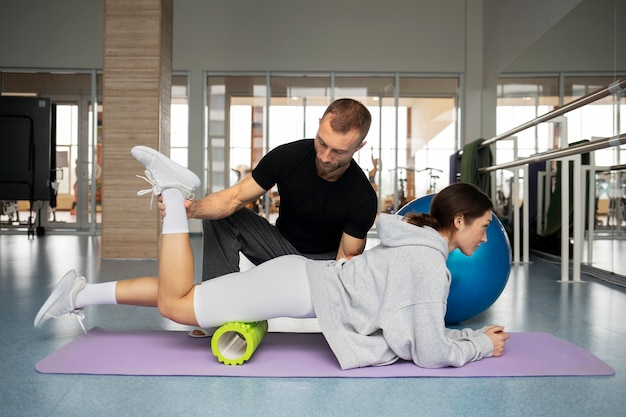
Modern sports medicine provides treatments tailored to the severity and location of the injury. Arthroscopic surgery uses small incisions and cameras to diagnose and repair joint damage. Non-surgical approaches, such as rest, ice, compression, elevation, and physical therapy, help restore strength, flexibility, and coordination. Imaging techniques, such as MRI and ultrasound, assist in accurately identifying injuries.
Advantages of arthroscopic procedures include:
- Smaller incisions reduce infection risk
- Less tissue damage speeds recovery
- Reduced pain and swelling after surgery
- Faster return to activities
- More precise visualization of joint structures
These methods aim to support recovery, restore function, and help athletes return to activity safely.
Evaluate Risks of Sports Injuries
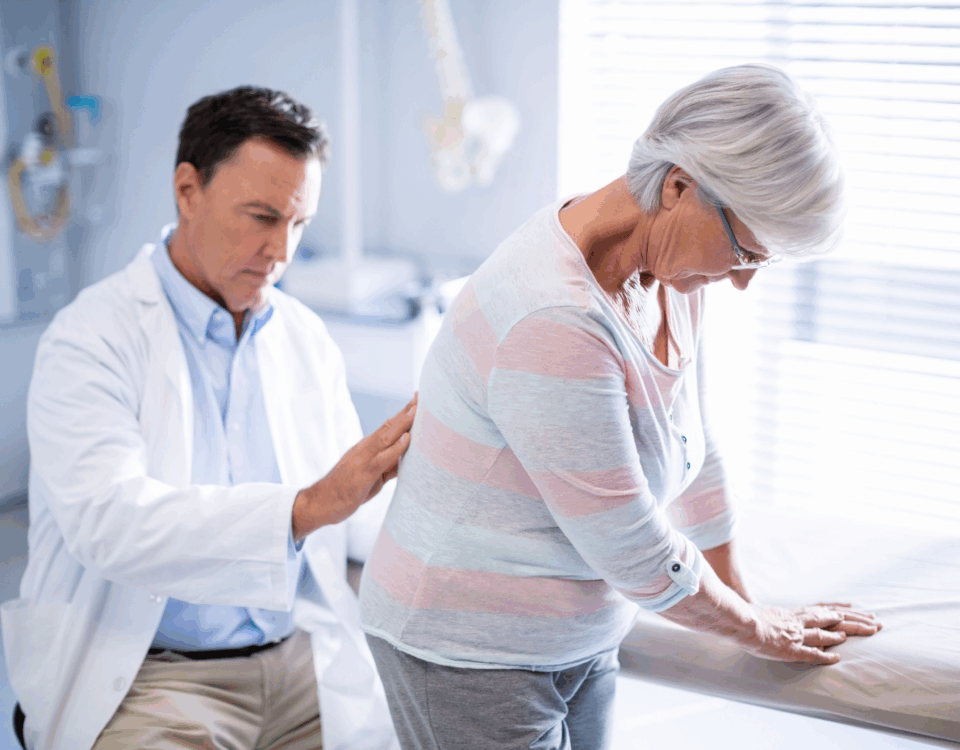
Understanding sports injury risks helps athletes make informed choices about their activities. Each sport has its own specific injury patterns, and personal factors such as age, fitness, and injury history influence the risk. Access to quality medical care can affect prevention and treatment outcomes. Discussing your individual risks and goals with a healthcare professional can guide safer participation.





